Crohn’s disease is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the digestive tract. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or background. There’s no cure for Crohn disease, but many people feel better by using the right treatments and making healthy lifestyle changes. In this article, we’ll explain Crohn disease in a simple way, including its symptoms, causes, and how to manage it.
What Is Crohn’s Disease?
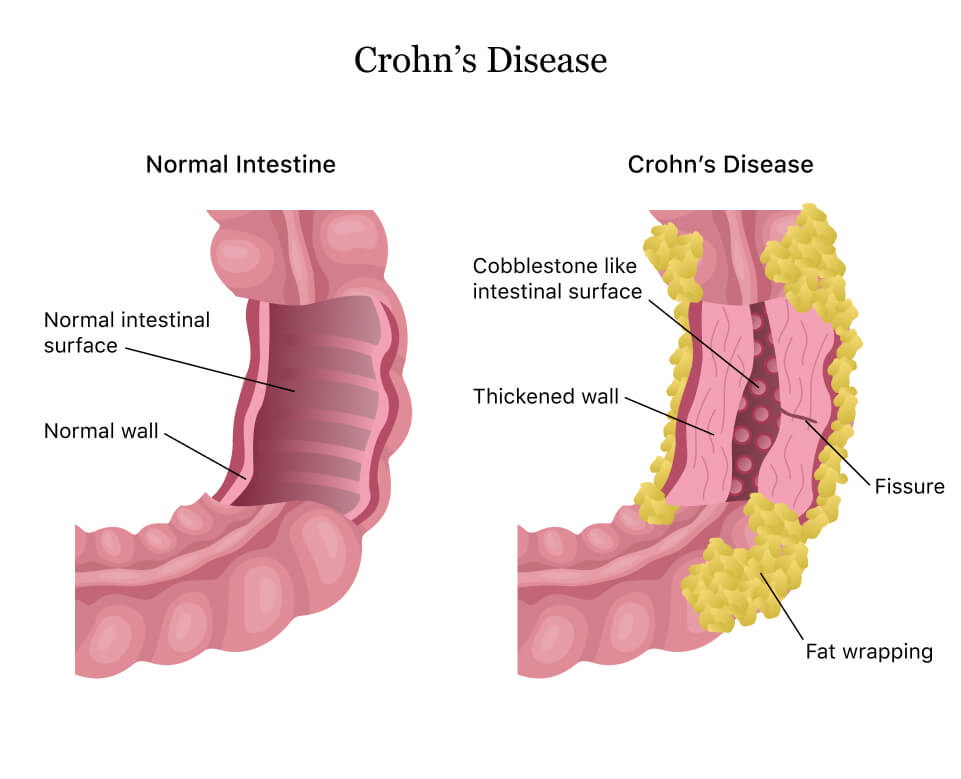
Crohn’s disease is a type of bowel disease that causes swelling in the digestive system. This swelling can happen anywhere in the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. But it usually affects the end of the small intestine and the start of the large intestine. Swelling can make the stomach walls thicker, leading to problems like narrow areas (strictures), small tunnels between organs (fistulas), or painful lumps filled with pus (abscesses).
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease can vary from person to person and may change over time. Common symptoms include:
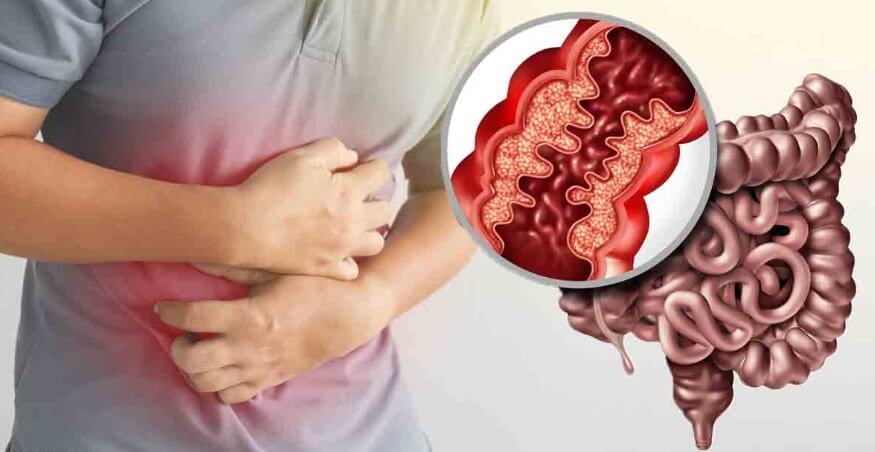
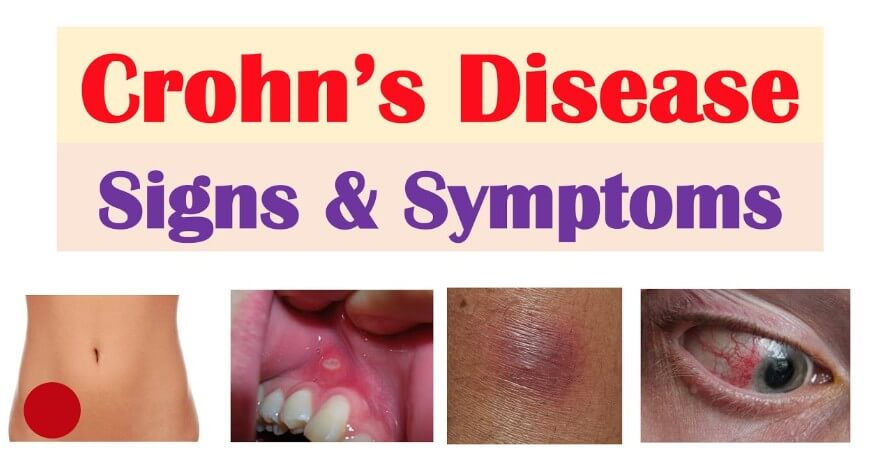
- Abdominal pain and cramping: Often in the lower right abdomen.
- Diarrhea: Sometimes accompanied by blood.
- Fatigue: Due to inflammation and nutrient malabsorption.
- Weight loss: Resulting from reduced appetite and nutrient loss.
- Fever: Often during flare-ups.
- Mouth sores: Painful ulcers inside the mouth.
- Reduced appetite: Leading to unintended weight loss.
- Perianal issues: Pain or drainage near or around the anus due to inflammation from a tunnel into the skin, called a fistula.
In serious cases, Crohn disease can also affect other parts of the body, causing problems like joint pain, skin rashes, eye swelling, or liver issues.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Genetics: A family history of IBD increases risk. Specific gene mutations, such as those in the NOD2/CARD15 gene, have been linked to Crohn disease.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An abnormal immune response may lead to inflammation in the GI tract.
- Environmental Factors: Diet, smoking, and certain medications can trigger or exacerbate symptoms.
- Microbiome Imbalance: Alterations in gut bacteria may play a role in disease development.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease involves a combination of:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: To assess symptoms and family history.
- Blood Tests: To check for signs of inflammation or anemia.
- Stool Tests: To rule out infections.
- Imaging Studies: Such as CT scans or MRIs to visualize the GI tract.
- Endoscopy: To look into the intestines to collect tiny samples to check for issues, doctors use a narrow tube with a camera.
Treatment Options
There’s no cure for Crohns disease, but treatments can help reduce swelling, control symptoms, and prevent flare ups.
Medications
- Aminosalicylates (5-ASAs): Anti-inflammatory drugs used for mild cases.
- Corticosteroids: Used for short-term flare-ups due to potential side effects with long-term use.
- Immunosuppressants: Such as azathioprine and methotrexate, to reduce immune system activity.
- Biologics: Target specific components of the immune system. Examples include:
- TNF inhibitors: Like infliximab and adalimumab.
- Integrin inhibitors: Such as vedolizumab.
- JAK inhibitors: Like upadacitinib, approved for moderate to severe cases.
Surgery
If the drug isn’t working or there are issues like tiny areas or tunnels between organs, surgery can be required. Procedures can include:
- Resection: Removing the diseased portion of the intestine.
- Strictureplasty: Widening narrowed areas of the intestine.
- Fistula Repair: Closing abnormal connections between the intestine and other organs.
However, surgery does not cure Crohns disease, and symptoms may recur.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
Managing Crohn’s disease involves more than just medication. Lifestyle and dietary changes can help control symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Dietary Adjustments: Work with a dietitian to find foods that make symptoms worse and make sure you’re getting enough nutrients. Common recommendations include:
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals.
- Avoiding high-fiber foods, spicy dishes, and dairy products if they cause issues.
- Ensuring sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals, possibly through supplements.
- Regular Exercise: Doing moderate exercise can help reduce stress and improve your overall health.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking can exacerbate symptoms and increase the risk of complications.
Coping and Support
Living with Crohn’s disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Support is crucial:
- Support Groups: Talking to others who have the same challenges can offer support and helpful advice.
- Mental Health Care: It’s important to control stress, anxiety, and depression because they can make the disease worse.
- Education: Understanding the disease empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care.
Prognosis

Crohn’s disease is a lifelong condition with periods of active disease and remission. Crohn disease can cause problems like blocked intestines, not getting enough nutrients, and a higher chance of colon cancer. But many people can manage it well with the right care and lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Crohn’s disease is a complicated condition that needs careful treatment. With better treatments and care that fits each person, those with Crohn disease can live active, happy lives. Early diagnosis, the right treatment, and support are key to managing it well.
FAQs
Q1: Can Crohn’s disease be cured?
A1: Currently, there is no cure for Crohn disease. However, treatments are available to manage symptoms and maintain periods of remission.
Q2: Is Crohn’s disease hereditary?
A2: Genetics play a role in Crohns disease. If a family member has the condition, you’re more likely to get it too, but other factors like your environment also play a role.
Q3: What are the common complications of Crohn’s disease?
A3: A higher rate of colon cancer, painful tearing around the small intestine, tiny gaps between organs, blocked intestines, and lack of food are some of the complications.
Q4: How can lifestyle changes help manage Crohn’s disease?
A4: Changing your diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can help control symptoms and make you feel better.
Q5: Is there a link between stress and Crohn’s disease?
A5: Stress doesn’t cause Crohn’s disease, but it can make symptoms worse and trigger flare-ups.
You May Read: You need to Know about Healthy Foods and Good Health in 2025












2 thoughts on “Crohn’s Disease: Need to know about Symptoms, Causes, and Management in 2025”